
HESI has a longstanding history of being a predictor of NCLEX® effectiveness. With changes to the NCLEX on the horizon, adding items to HESI with Next Generation NCLEX (NGN) in mind was important. Over 35,000 HESI test-takers have taken NGN items, with over 144+ NGN items actively piloted on HESI exams. “NGN for All” integrates NGN items in everyone’s HESI Next Generation exams where content is available. Once students complete an exam, they’ll see reporting on how they performed on these new items. Also, until the validity study is completed, the items will not impact the student’s final HESI scores. The exposure to the new NGN style items will allow you to prepare students early and put your program one step ahead towards being NGN-ready.
Here are recommendations, best practices, and tips to prepare students taking HESI exams with NGN content and questions:
Understand Why the Test Format is Changing
- Traditionally, the NCLEX presents items through a snapshot in time, with one patient and one scenario to test students’ fundamental knowledge. With the new NGN, items will feature the same patient over time through unfolding case studies. This will test students’ ability to think deeper about the patient and better reflect the reality of what they’ll see as a nurse.
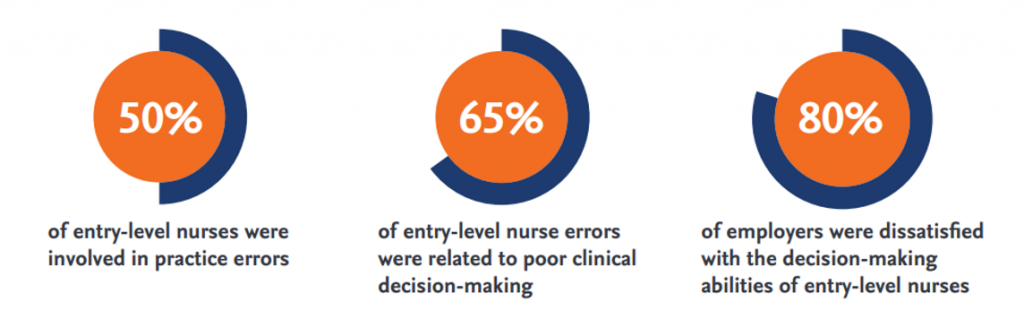
- It’s never too early to introduce students to data—give students the information and research behind why the NCLEX test design is changing with the stats that students are not practice-ready. Here are three easy stats to share that emphasize why these changes are so important:
- Explain to students how the NGN is different from the current NLCEX by taking students to the NCSBN website and going through the new item types. They should also understand how the cognitive skills in the NCSBN Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (NCJMM) will be measured. There’s no such thing as too much exposure when it comes to NGN!
Before Students Practice NGN Item Types
- Bring clinical to the classroom—have discussions about patients to get them into that thought process that will be applied on the exam and push them to find the gaps in the knowledge.
- Ask difficult questions in the learning environment, whether that’s the classroom or lab, to engage students in the thinking process that will enhance clinical judgment and prepare them to test their knowledge. If they get it wrong, that’s ok—it’s better for students to be wrong in the classroom instead of in the clinical setting.
Working With Students After the Exam
- Although the select HESI exams that feature NGN item types are not scored or counted as part of their final HESI grade, remediation is still tied to these answers. Each cognitive skill featured in Layer 3 of the NCJMM is tagged through question content, so if a student misses a question mapped to “recognize cues” remediation will be provided for that cognitive skill.
- Require students to complete all of the associated remediation after their HESI exam to strengthen areas of weakness, including the cognitive skills they will be tested on during the NGN.